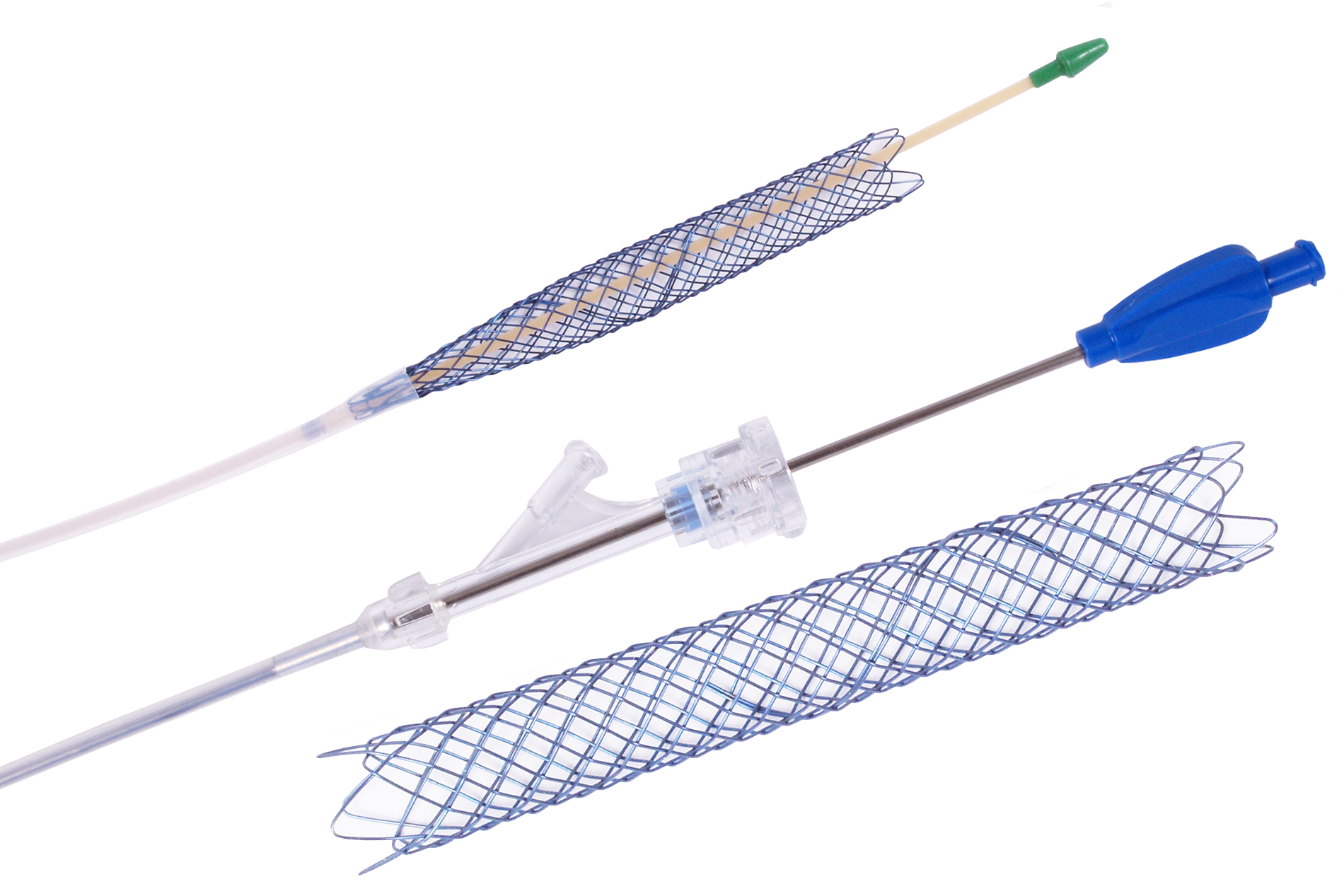
Nitinol Tracheal Stents
What is it?
The stent is a highly flexible metal mesh designed to reconstruct the trachea. A properly placed tracheal stent relieves severely constricted airways and prevents trachea from collapsing. Treatment of trachea collapse is a difficult and often symptomatic treatment is administered, which will not remove the primary cause of coughing and dyspnoea. Pharmaceutical drugs are used in the initial stage of collapse, in more advanced stages a treatment is needed – we insert a tracheal stent.